Niobium CB-752
Nb752 is a medium-strength niobium alloy. It uses niobium as the base metal, adding no more than 10% tungsten, zirconium and other metal elements and a small amount of carbon to form a solid solution strengthening and a small amount of ZrO2 and (Nb, Zr) C precipitation strengthening a combination of niobium alloy.
At room temperature, the strength of Nb752 is 450-600MPa, the elongation δ=20%-30%, and it still has a fairly high strength between 1000-1400°C. Because Nb752 is more sensitive to interstitial elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc., its DBTT is relatively high, and the DBTT in the welding state is generally above room temperature. Therefore, during production and use, the pollution of hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen must be strictly controlled, and the oxygen and nitrogen content must be controlled below 80x10^(-6).
| Thermal conductivity of CB752 | |
| Temperature, ℃ | Thermal conductivity, K/cm.s.℃ |
| 260 | 0.091 |
| 538 | 0.107 |
| 816 | 0.116 |
| 1093 | 0.119 |
| 1204 | 0.12 |
| 1316 | 0.121 |
Main chemical composition of Cb752 (mass fraction)
| Grade | Chemical Composition / % | Chemical Composition / 10-6 | |||||||||
| Nb | W | Mo | Ta | V | Hf | Zr | Ti | C | O | N | |
| Cb752 Nb-10W-2.5Zr |
Balance | 9~11 | 2~3 | 10 | <200 | <200 | |||||
Physical properties of Cb752
| Grade | Component | Density /g.cm-3 | Melting point /℃ | Linear expansion coefficient /℃ | Recrystallization temperature /℃ | Annealing temperature /℃ | Elongation brittle transition temperature /℃ |
| Cb752 | Nb-10W-2.5Zr-0.05Mo-0.15Ta-0.1Hf | 8.83 | 4.5(1203℃) | 1023~1371 | 982~1093 | -196 |
Mechanical properties(21℃)of CB752 (Nb-10W-2.5Zr)
| Grade | Component | Elastic Modulus /MPa | tensile strength /Mpa | Yield Strength /Mpa | Elongation (gauge length 50.8mm)% |
| Cb752 | Nb-10W-2.5Zr-0.05Mo-0.15Ta-0.1Hf | 112 490 | 562.5 | 471.1 | 27 |
Forms of Cb752 We Can Provide
Material properties of CB752 (Nb-10W-2.5Zr)
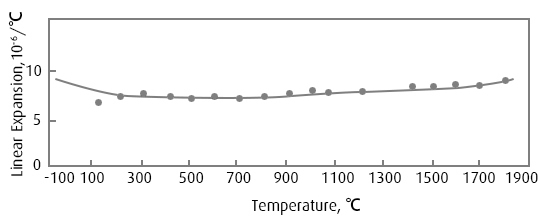
| Linear expansion coefficient of CB752 | |
| Temperature range, ℃ | Average coefficient of thermal expansion, 10-6/℃ |
| 20~93 | 6.85 |
| 20~538 | 7.2 |
| 20~871 | 7.56 |
| 20~1093 | 7.93 |
| 20~1204 | 8.11 |
| High temperature radiation coefficient of CB752 | |
| Test temperature, ℃ | eλ |
| 1039 | 0.32 |
| 1214 | 0.35 |
| 1357 | 0.36 |
| 1612 | 0.35 |
| 1740 | 0.36 |
| 1795 | 0.37 |
| 1963 | 0.33 |
| P.S.: 5mm diameter bar (as machined), single color λ=0.65μM | |
| High temperature performance of CB752 | ||||||
| Grade | Component | Forms | Temperature/℃ | Tensile Strength/MPa | Temperature/℃ | Breaking Strength/MPa |
| Cb-752 | 10W、12.5Zr | Sheet | 1316 | 182.8 | 1093 | 112.5 |
| Notched tensile properties of CB752 | ||
| Plate thickness, mm | Tensile strength, kg/mm2 | 0.2% Yield Strength, kg/mm2 |
| 0.34 | 52 | 47.8 |
| 52.6 | 49.4 | |
| 53.4 | 48.7 | |
| 55 | 52 | |
| 54.3 | 48.5 | |
| 0.46 | 62 | 54 |
| 60.4 | 53.3 | |
| 60.7 | 52.1 | |
| 61 | 53.8 | |
| 62.7 | 55.8 | |
| Room temperature tensile properties after CB752 coating | |||||
| Coating system | Zr-V-Si(melting) | Ti-Cr-Si(inclusion)① | |||
| Basic material | Add coating | Add coating | Add coating+1300℃ | Add coating+1200℃ | |
| Tensile strength, kg/mm2 0.2% yield strength, kg/mm2 Elongation, % |
55.5 | 44.5 | 45 | 48 | 48 |
| 43.5 | 34 | - | - | - | |
| 28.5 | 13.5 | - | >30.0 | >16.0 | |
| Note | 0.8mm sheet, annealed at 1300℃ for 1 hour | 1mm sheet, annealed at 1300℃ for 1 hour | |||
| ① Short sample, K=5.65 | |||||
| High temperature tensile properties after CB752 coating | ||||||||
| Test temperature, ℃ | 800 | 1200 | 1400 | 1600 | ||||
| Basic Material | After coating | Basic Material | After coating | Basic Material | After coating | Basic Material | After coating | |
| Tensile strength, kg/mm2 0.2% yield strength, kg/mm2 Elongation, % |
45.5 | 30 | 24 | 22.5 | 14.5 | 12 | 8 | 7.5 |
| 29 | - | 19.5 | 19.5 | 12.5 | 10.5 | 7.5 | 6.5 | |
| 15 | - | 63.5 | 33 | 91 | 42.5 | 78.5 | 91 | |
| Note:Plate thickness 0.8 mm, cold rolled + 1200 ℃ annealing for 1 hour, Zr-V-Si sintered coating, stretching direction is transverse | ||||||||
| Durable tensile properties at 1200℃ after CB752 coating | |||||||||||
| Coating system | Basic material① | Zr-V-Si | Ti-Cr-Si | ||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Specimen stress, kg/mm2 duration, hours |
10 | 10 | 7 | 8 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 10 | 8 | 7.5 | 7 | 7 |
| 28 | >28 | 52.3 | 14.3 | 23 | 23 | 16 | 6.8 | 79 | 110 | >111.4 | |
| Notes | 0.8mm sheet, annealed at 1200℃ for 1 hour | 1.0mm sheet, annealed at 1200℃ for 1 hour | |||||||||
| ①The vacuum degree is 1.0x10-4mm Hg, the test atmosphere is the atmosphere, and the stretching direction is transverse. | |||||||||||
| Welding performance of CB752 | ||||||
| Welding method | Basic material | Electron beam welding | Pulse argon arc welding | |||
| Test temperature, ℃ | Room temperature | Room temperature | 1200 | 1400 | 1600 | Room temperature |
| Tensile strength, kg/mm2 0.2% yield strength, kg/mm2 Elongation, % |
57 | 57 | 20.5 | 9.5 | 8 | 50 |
| - | 45 | - | - | - | ||
| 30 | 19 | 8 | <6.5 | 24.5 | 9~16 | |
| Creep properties of CB752 (total creep, %) | |||
| Alloys | Test temperature,℃ | ||
| 1093 | 1204 | 1316 | |
| CB752 (Nb-10W-2.5Zr) | 0.53 | 3.57 | 12 |
Antioxidant properties of CB752 (Nb-10W-2.5Zr)
1. Add elements with higher atomic valence than niobium, such as molybdenum, tungsten, iridium and vanadium, etc., to overcome the lack of cations in the oxide scale, so as to reduce the diffusion of oxygen through the oxide scale to the oxide and metal interface.
2. Add elements with small ionic radius, such as vanadium, molybdenum, tungsten and aluminum, etc., to reduce the volume ratio of oxide to metal and prevent oxide peeling.
3. Add a large amount of solute elements, such as molybdenum, tungsten, tantalum, titanium and hafnium, etc., to improve the mechanical properties and chemical stability of the oxide scale.
Application of Cb752
Nb752 is suitable for manufacturing riveted and fastened components, such as skins, bolts, nuts, etc.
High temperature and high strength, used in the aerospace industry.


 +86 13120915623
+86 13120915623